In this blog, I’ll look at what it takes to create an enterprise geodatabase for HANA, enable it and copy some feature classes from another enterprise geodatabase into the HANA one. I’ll discuss the creation and loading of utility models in another post.
As many of you know, the ArcGIS platform has been able to access tables in HANA using query layers since ArcGIS Server and Desktop – 10.3 and Pro 1.2 were released in 2014. This enabled spatial data in HANA to be consumed and updated by the ArcGIS platform. As of ArcGIS Server 10.3.1, feature services against HANA were supported. This is commonly known as an agile spatial datamart or “sidecar” scenario.
The second scenario is creating an enterprise geodatabase in HANA. Esri is referring to this scenario as Esri ArcGIS on HANA.
The first release of the enterprise geodatabase for HANA will support the following:
◉ subtypes/domains
◉ relationship classes
◉ attachments
◉ editor tracking
◉ non-versioned archiving
◉ offline editing with sync capabilities
◉ new service based long transaction model for editing
◉ utility network
Although this release supports the new services based utility network, support for geodatabase topology and editable network datasets are planned for future releases of ArcGIS Pro. Examples include Parcel Fabric.
Assuming you have installed or have access to ArcGIS Enterprise 10.6 and Pro 2.1, the steps for creating an enterprise geodatabase are:
1. Install and configure the SAP HANA 64 bit ODBC drivers (part of the SAP HANA Client) on both the Enterprise and Pro instances. Use the same connection name on the Enterprise instance. Record the name of your ODBC connection for later (step 6)
2. Using the HANA Cockpit or HANA Studio, create an SDE user in your HANA instance. The SDE user will need CATALOG READ permissions. If you don’t have USER ADMIN privs, get the HANA DBA to create the SDE user for you.
3. Test your ODBC connection using the SDE user from both the Pro and Enterprise instances
4. Start ArcGIS Pro and create a new project
5. Right click the Databases group in the Catalog pane on the right and select New Database Connection
As many of you know, the ArcGIS platform has been able to access tables in HANA using query layers since ArcGIS Server and Desktop – 10.3 and Pro 1.2 were released in 2014. This enabled spatial data in HANA to be consumed and updated by the ArcGIS platform. As of ArcGIS Server 10.3.1, feature services against HANA were supported. This is commonly known as an agile spatial datamart or “sidecar” scenario.
The second scenario is creating an enterprise geodatabase in HANA. Esri is referring to this scenario as Esri ArcGIS on HANA.
The first release of the enterprise geodatabase for HANA will support the following:
◉ subtypes/domains
◉ relationship classes
◉ attachments
◉ editor tracking
◉ non-versioned archiving
◉ offline editing with sync capabilities
◉ new service based long transaction model for editing
◉ utility network
Although this release supports the new services based utility network, support for geodatabase topology and editable network datasets are planned for future releases of ArcGIS Pro. Examples include Parcel Fabric.
Assuming you have installed or have access to ArcGIS Enterprise 10.6 and Pro 2.1, the steps for creating an enterprise geodatabase are:
1. Install and configure the SAP HANA 64 bit ODBC drivers (part of the SAP HANA Client) on both the Enterprise and Pro instances. Use the same connection name on the Enterprise instance. Record the name of your ODBC connection for later (step 6)
2. Using the HANA Cockpit or HANA Studio, create an SDE user in your HANA instance. The SDE user will need CATALOG READ permissions. If you don’t have USER ADMIN privs, get the HANA DBA to create the SDE user for you.
3. Test your ODBC connection using the SDE user from both the Pro and Enterprise instances
4. Start ArcGIS Pro and create a new project
5. Right click the Databases group in the Catalog pane on the right and select New Database Connection
6. The following dialog will appear. First, select SAP HANA as the Database Platform. Then use the ODBC connection name you recorded earlier (when you later register the enterprise geodatabase with ArcGIS Enterprise, you’ll use the same ODBC data source name). Specify the password for the SDE user.
7. If you’ve correctly done the proceeding steps, you should now have a connection to the SDE database in HANA. In HANA, each user has its own schema.
8. Now, you’ve reached the cool part – actually enabling a HANA database to be an enterprise geodatabase. Note that the enterprise geodatabase must be owned by the SDE user. You’ll need a keycode file from your Enterprise instance that authorizes you to enable HANA as an enterprise geodatabase. It is typically located as shown below on your Enterprise instance
C:\Program Files (x86)\ESRI\License10.6\sysgen
9. Copy the keycode file over to your Pro instance. You’ll provide the keycode file path in the Authorization File field and the specify the database connection you created in Step 7 above. Click run and in about 5 seconds, you’ve successfully enabled a HANA enterprise geodatabase.
10. Now, I’ll copy some feature classes from another enterprise geodatabase using the Import geoprocessing tool. You’ll first need to create a database connection to that database like what was done in Steps 5 and 6. You’ll specify the database connection to the other enterprise geodatabase, the feature class(es) you want to import and the target (the HANA enterprise geodatabase or a feature dataset inside it). Click Run and in a few minutes, you’ve easily copied feature classes into your new HANA enterprise geodatabase. Of course, the more feature classes you copy, the longer the Import will take…
So that’s it… assuming you’ve installed ArcGIS Enterprise 10.6 and Pro 2.1 and installed the ODBC 64 bit drivers, the rest of the steps I did above took about 10 minutes. Once you’ve enabled the geodatabase (Step 9), you can easily copy additional feature classes or feature datasets (a dataset is simply a group of feature classes – you can create one with the Create Feature Dataset geoprocessing tool in less than a minute.)
I went on to create and share a webmap to ArcGIS Enterprise. I navigated to Portal and simply right clicked and selected Add and Open as shown here:
…and the following map was created in ArcGIS Pro.
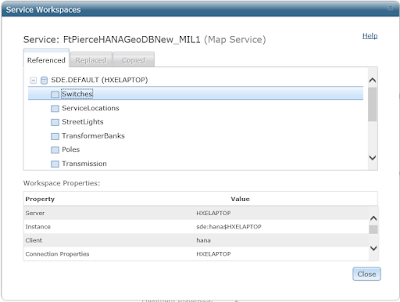
The above map uses map services served up by the ArcGIS Enterprise instance – which is obtaining the geometries from the HANA enterprise geodatabase. Just to make sure, I logged into the ArcGIS Server Manager on the ArcGIS Enterprise instance and looked at the map service used by the above map:
From here, there’s a lot you can do – you can author maps and utilize the advanced ArcGIS enterprise geodatabase features – and do all of that against an enterprise geodatabase in HANA…starting early next year. All-in-all, a great reason for 2018 to hurry up and arrive!